You can find more videos profiling graduate acousticians from #ExploreAcoustics.
What science and engineering jobs are there in sound?
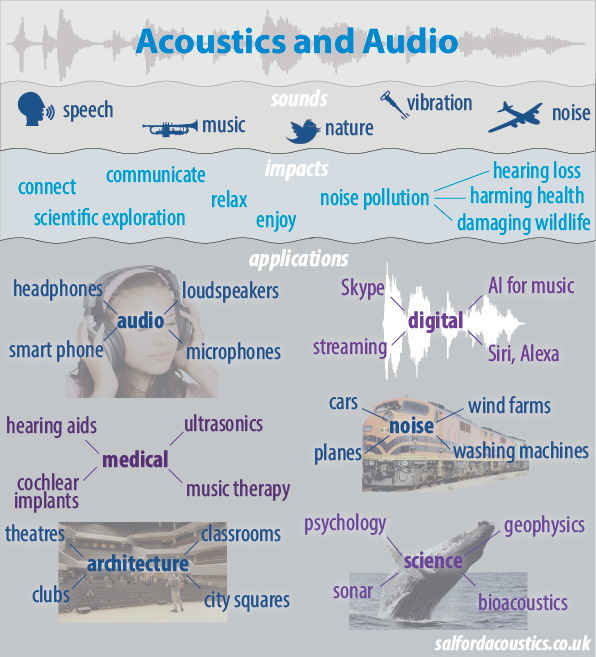
Sound is everywhere and central to our lives, so many different scientific and engineering disciplines carry out work in acoustics. You probably own a mobile phone that is stuffed full of audio engineering to make it work as a phone, music player and video recorder. But acoustics goes beyond audio to include the design of classrooms for good communication between teacher and pupils, ultrasonic imaging in medicine, the control of noise from machines, etc. You can do a job that improves peoples’ lives.
You’ll find much more about what acoustical and audio engineers do, as well as acoustic scientists on these Wikipedia pages:
Career profiles
There are a growing number of career profiles on this website linked from the curriculum material, showing how real Acoustical and Audio Engineers use sound physics in their jobs. They are:
Noise and vibration
- Elle Kalavsky works on new materials to absorb sound, and in the past has done noise monitoring at Glasto.
- Vicky Stewart works to reduce environmental noise and vibration.
- Naomi Tansey and Nathan Thomas both work at Dyson reducing noise and vibration in their products.
Digital technology
- Tony Churnside looks after the technology that drives BBC radio stations and creates innovative radio programmes.
- Guy Nicholson uses machine learning to improve how sound is processed by silicon chips at Google.
- Jose Maria Marin works for Amazon Alexa Automotive getting voice activated technologies into cars.
Architecture and building acoustics
- Trevor Cox designs acoustic materials for concert halls to make music sound better.
- Wenda Nuridahissan develops products to improve a buildings acoustics and sustainability.
- Tomasz Galikowski provides advice on reducing noise and vibration in the built environment.
Cars
- Ben West works on reducing noise created by air flowing around Bentley cars.
- Lucy Diggle is responsible for the sound quality of the sound systems in Jaguar and Land Rover cars
Hearing
- Emma Shanks, who works to reduce hearing loss at work places due to excessive noise.
- Teli Chinelis assists the courts in cases of alleged harm due to noise and vibration at work.
- Magnus Woodgate writes software to improve the sound from hearing aids
Traits of an acoustical and audio engineer
- Creative ● Innovative ● Attention to detail
- Patience ● Team player ● Technical and mechanical knowledge
- Natural curiosity ● Numerical skills ● Logical thinking
- Problem solving ● Ownership ● Good communication skills
For a STEM acoustical engineer starting salaries typically range from £21,000 to £25,000 . Currently there are more jobs available than graduates with the right qualifications.
Other sources of career information
- Explore Sound is a useful resources from the Acoustical Society of America.